Strengthening operational technology security by merging compliance protocols with cybersecurity strategies
Operational Technology (OT) security has become an essential component of modern industries to protect critical infrastructure and ensure smooth business operations. However, integrating compliance protocols into OT security is vital to achieving a more robust defense against cyber threats. This article delves into the importance of combining compliance and cybersecurity strategies for OT security and provides insights into implementing these measures effectively.
Understanding Operational Technology (OT) Security
Operational Technology (OT) refers to the hardware and software systems that manage industrial control processes, equipment, and machinery. In contrast to Information Technology (IT), OT deals with the real-time operations of physical devices and processes. With the increasing digitalization and interconnectivity of industries, OT security has become paramount for organizations to protect their critical infrastructure and ensure smooth business operations.
The Importance of Integrating Compliance into OT Security
Compliance is essential to cybersecurity, as it involves adhering to legal and regulatory requirements, industry standards, and best practices. Integrating compliance into OT security ensures that organizations maintain a strong security posture while meeting their legal obligations. This integration not only helps to mitigate risks and vulnerabilities but also fosters trust with clients, partners, and regulatory bodies. Compliance standards are often regional, with localized legal variations in operational standards and requirements.
Aligning Compliance with Cybersecurity Strategies
To effectively integrate compliance into OT security, organizations must align their cybersecurity strategies with relevant legal and regulatory requirements, industry standards, and best practices.
This alignment involves:
- Identifying applicable regulations: Organizations must identify the specific legal and regulatory requirements relevant to their industry, as well as any additional guidelines and standards applicable to their OT systems.
Below is a list of a few of the possible legal compliance standards and guidelines for operational technology cybersecurity, along with links to their official websites: - NIST SP 800-82: Guide to Industrial Control Systems (ICS) Security
- IEC 62443: Industrial Communication Networks – Network and System Security
- ISO/IEC 27001: Information Security Management Systems
- NERC CIP: North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection
- CIS Critical Security Controls
- ISA/IEC 62443: Security for Industrial Automation and Control Systems
- GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation (European Union)
- HIPAA: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (United States)
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- CCPA: California Consumer Privacy Act (United States)
Please note that this is just a small cross-section of industry standards, and some of these regulations are not specific to operational technology but are generally relevant to cybersecurity. We recommend that security teams carefully review the standards and regulations that apply to their specific industry and operational technology systems to ensure compliance.
- Assessing current cybersecurity posture: Organizations should conduct a thorough assessment of their existing cybersecurity measures, identifying any gaps or weaknesses that may hinder compliance.
- Developing a roadmap: A comprehensive roadmap should be developed, outlining the necessary steps to align cybersecurity strategies with compliance requirements. This includes setting objectives, assigning responsibilities, allocating resources, and establishing timelines.
- Implementing and monitoring progress: Organizations must implement the defined roadmap and continuously monitor their progress in achieving compliance, making adjustments as needed.
Establishing a Comprehensive Compliance Program
Organizations should establish a comprehensive compliance program that encompasses various aspects of OT security. This includes:
- Governance and management: Establish a governance structure and a compliance management team responsible for overseeing and implementing the compliance program.
- Policies and procedures: Develop clear and concise policies and procedures that outline the organization’s approach to compliance, including roles and responsibilities, risk management, reporting, and incident response.
- Training and awareness: Implement training programs to educate employees about their roles and responsibilities regarding compliance, as well as the importance of adhering to the organization’s policies and procedures.
- Auditing and monitoring: Regular audits and monitoring should be conducted to ensure compliance with the established policies and procedures, identify potential issues, and track progress toward compliance objectives.
- Continuous improvement: The compliance program should be continuously improved and updated to reflect changes in legal and regulatory requirements, industry standards, and best practices.
Implementing a Risk-based Approach to Compliance
A risk-based approach to compliance helps organizations prioritize their efforts and allocate resources efficiently. This approach involves:
- Identifying risks: Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that may impact the organization’s OT systems.
- Prioritizing risks: Evaluate the identified risks based on their likelihood and potential impact, prioritizing those that pose the most significant threats to the organization’s OT security and compliance.
- Implementing controls: Develop and implement appropriate controls to mitigate the prioritized risks, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, industry standards, and best practices.
- Monitoring and reviewing: Continuously monitor and review the effectiveness of the implemented controls, making adjustments as needed to address emerging risks and maintain compliance.
Adopting a Holistic Approach to OT Security and Compliance
Organizations should adopt a holistic approach to OT security and compliance, integrating various components to create a comprehensive security strategy. This involves:
- Technology: Implement state-of-the-art technologies, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, lateral movement protection, encryption, and zero trust methodologies, to protect OT systems from cyber threats.
- People: Develop a security-aware culture within the organization, emphasizing the importance of compliance and cybersecurity best practices among employees.
- Processes: Establish standardized processes for managing and maintaining OT security and compliance, including incident response, risk assessment, and continuous improvement.
- Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT and OT teams, as well as with external partners and regulatory bodies, to ensure a unified approach to cybersecurity and compliance.
Leveraging Third-party Expertise
Organizations can benefit from engaging third-party experts to help them integrate compliance into their OT security strategies. These experts can provide valuable insights and support in areas such as:
- Regulatory landscape: Third-party experts can help organizations navigate the complex regulatory landscape, ensuring that they understand and comply with all relevant legal and regulatory requirements.
- Risk assessment: External experts can assist in conducting thorough risk assessments, identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities, and prioritizing them based on their likelihood and potential impact. Baselining current activity can clarify an organization’s security posture for measuring risk and possible security violations.
- Compliance program development: Third-party experts can help organizations develop and implement comprehensive compliance programs, encompassing governance, policies and procedures, training and awareness, and auditing and monitoring.
- Continuous improvement: External experts can provide ongoing support in updating and improving the organization’s compliance program, ensuring that it remains aligned with evolving legal and regulatory requirements, industry standards, and best practices.
Considering the Purdue Model for OT Security Best Practices
As CISOs and cybersecurity team leaders, staying informed about the latest frameworks and methodologies for securing Operational Technology (OT) systems is essential. One such model gaining popularity is the Purdue Model for OT security. This framework, originally developed in the early 90s for manufacturing control systems, is now widely adopted across various OT environments. The key to its effectiveness lies in its hierarchical structure, which comprises seven levels, providing a clear separation between the enterprise and OT domains.
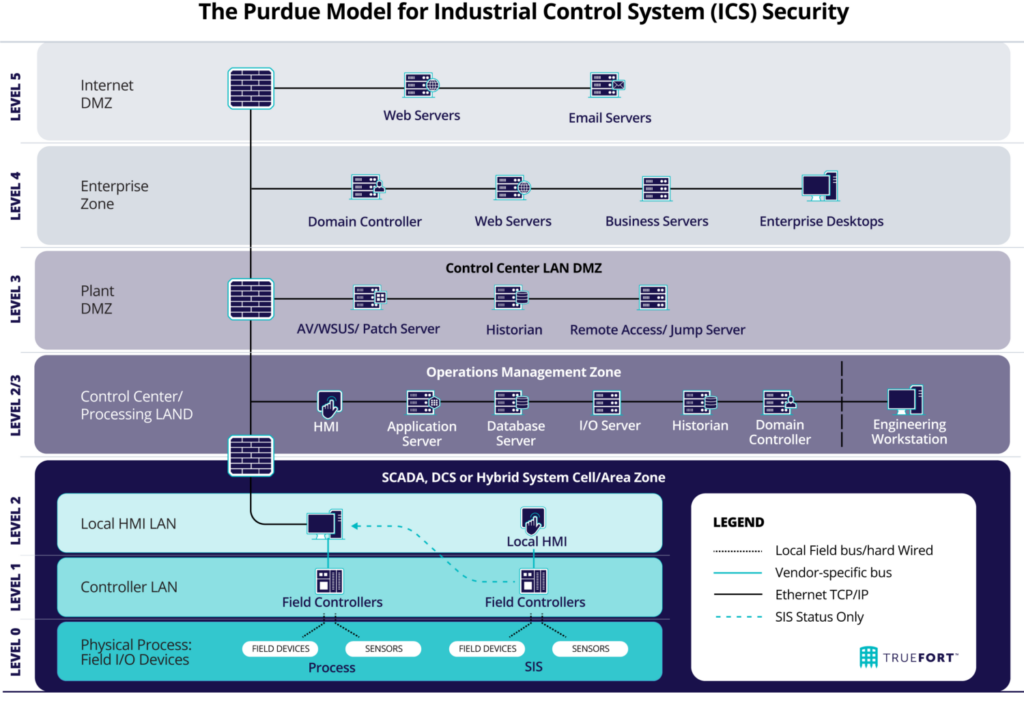
For a more in-depth understanding of the Purdue Model, consider these resources:
- What Is the Purdue Model for Industrial Control System (ICS) Security?
- Industrial Network Security: Securing Critical Infrastructure Networks for Smart Grid, SCADA, and Other Industrial Control Systems by Eric D. Knapp and Joel Thomas Langill.
Key takeaways of the Purdue Model for OT security include:
- Clear separation of concerns: The model’s levels ensure that IT and OT networks are effectively segregated, reducing the potential for security incidents.
- Defense-in-depth strategy: Multiple layers of security controls help prevent unauthorized access and contain potential threats.
- Enhanced visibility: With a well-defined structure, it becomes easier to monitor and detect anomalies in the network.
The Purdue Model for OT security can help CISOs and cybersecurity team leaders establish a robust and resilient OT security posture, ensuring the safety and integrity of critical infrastructures. By adopting this framework, organizations can effectively mitigate risks and enhance their ability to respond to evolving cybersecurity threats in the OT landscape.
In summary
Integrating compliance into OT security is crucial for organizations to protect their critical infrastructure, ensure smooth business operations, and maintain a strong security posture. Organizations can effectively merge compliance protocols with their OT security strategies by aligning compliance with cybersecurity strategies, establishing a comprehensive compliance program, implementing a risk-based approach, adopting a holistic approach, leveraging third-party expertise, and considering the Purdue Model. This integration mitigates risks and vulnerabilities, and fosters trust with clients, partners, and regulatory bodies, ultimately contributing to the organization’s long-term success.
At TrueFort we have entered into a strategic partnership with Armis, one of the leading providers of asset visibility and security solutions. Our collaboration means that there is now a single platform combining business and asset intelligence to manage the security challenges resulting from the growing number of connected OT and IT devices and control systems. If you want to discover more about our strategic alliance, please see our Armis/Truefort partnership announcement.





